For The Transit Fans: Technology Profile: Engine Types
There are many different types ways to build an engine, each with distinct differences and qualities.

The Ford Focus RS uses Ford's Duratec Engines (Spring 2016 US Release)
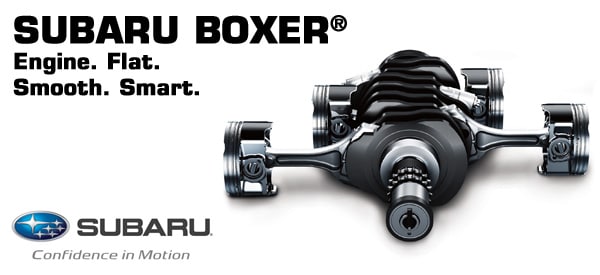
Subaru Flat 4 Boxer Engine
Boxer Engines: Boxer Engines, also called "Flat Engines" because of their flat and usually compact profile, use Horizontally Opposed pistons which when moving looking like the gloves of two boxers in a match hence the name. Cars using Boxer Engines typically have a lower center of gravity because they are usually lighter and smaller meaning they can be placed lower and farther back in the engine bay. This gives the car a much sportier handling characteristic. Because of the Horizontal layout configuration, Boxer Engines are the only engine type which do not require a balance shaft to hold counterweights because there are no unbalanced forces in its four stroke cycle as long as each bank has the same number of cylinders. Although most car fans do not consider this a drawback, one main characteristic of Boxer engines is that they tend to be louder than engines of other types. When the Engine runs with Engine Block Headers of Unequal Length, a distinctive rumble is heard from its exhaust caused by its firing order. There are currently two Manufacturers who make extensive use of this type of engine, Subaru of Japan and Porsche in Germany.

Volkswagen VR6 Engine
VR6 Engines: VR6 Engines utilize a complex narrow angle V shape in which work between the cylinders is shared with common parts.The name comes from the combination of the German words for V-Motor and Inline Engine. When 6 cylinders are present there is only one cylinder head for two rows of cylinders. Although vastly different VR6 Engines are able to use the same firing order as a Straight Six Engine. As Volkswagen were the original creators of this technology there are also the primary users, coming into its cars in the 1980's.

Rotary Engine 4 Stroke Diagram
Wankel Engine: Also called Rotary Engines, do not use pistons within a cylinder head to perform the four stroke cycle. Wankel Engines use a three sided triangular shaped "rotor" which spins on an axis performing all of the steps in the cycle in a completely different way. Unlike pistons which are constantly heated and cooled, the rotors are being heated and cooled simultaneously. Developed by German Engineer Felix Wankel this engine type has seen most of its commercial success with Japanese manufacturer Mazda in both its sports cars and race cars. Wankel Engines typically can reach far higher RPMs that pistons and this means they create far more heat than other types of engines. However this means that fuel economy usually suffers and Wankel engines are far more prone to sealant and leaking problems.

Dodge Challenger SRT Hemi Engine
Hemi Engines: Hemi which is short for Hemispherical Combustion Chamber uses these chambers which use a domed shaped cylinder head. In order to achieve domed shaped cylinder heads the engine block must use a wedge shaped design. The primary reason for using a Hemi engine is that the design allows for a higher mechanical compression ratio. This allows for maximum power at higher RPMs. However Hemi Engines have many drawbacks. They are heavy, and the wedge shaped engine is very large which is why it has been nicknamed the Elephant Engine. They also require more parts and complex assembly and can only use 2 valves per cylinder. Because the engines are heavy and very big the cars they usually find themselves in are as well. Many manufacturers around the world have experimented with Hemi Engines and they were very prominent in the early 1900's but have seen the most commercial success with Chrysler which uses them in their Dodge brand as well.

Honda Intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control (VTEC) Dual Overhead Cam (DOHC)
VTEC Engines: Invented by an Engineer at Honda, VTEC Engines are a solution to a problem created by Japanese Law. In Japan, cars are taxed based on Engine Displacement which basically works out to, cars with larger engines pay more in road taxes. This means cars in Japan typically have smaller engines. This has lead to car manufacturers to devise ways to milk more power out of smaller engines. Several designs were used such as Rotary Engines. Another solution was to add a turbocharger which is still the preferred method to get more power out of smaller engines. Ikuo Kajitani an Engineer at Honda, created the VTEC engine. These engines use two camshaft profiles and timing of the valves to improve power. Most are Natrually Aspirated and do not use turbochargers.
Diesel Engines:
-
 2
2




0 Comments
Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Join the herd!Sign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now